Most Blue Badge Guides, when conducting a tour of London, will give priority to what people can see. Occasionally, however, they will mention a building that has been lost to fire, bombing or development. One such is the Crystal Palace, originally found in Hyde Park.
This famous building was the home to the Great Exhibition of 1851 when tourism started in earnest in Britain. A midlands businessman Thomas Cook, who had previously organised day tours for fellow Baptists in Leicestershire, began selling trips on the newly built railways so people could come to London to see all the treasures housed at the Palace.
The building had originally been called ‘The Great Shalimar’ and was designed by Joseph Paxton, also from the midlands. He had impressed William Cavendish, the Duke of Devonshire and been given a position at the family home Chatsworth House, where he designed greenhouses in which were grown pineapples and bananas. The Cavendish banana, first developed by Paxton, is now the world’s most widely consumed version of the fruit.
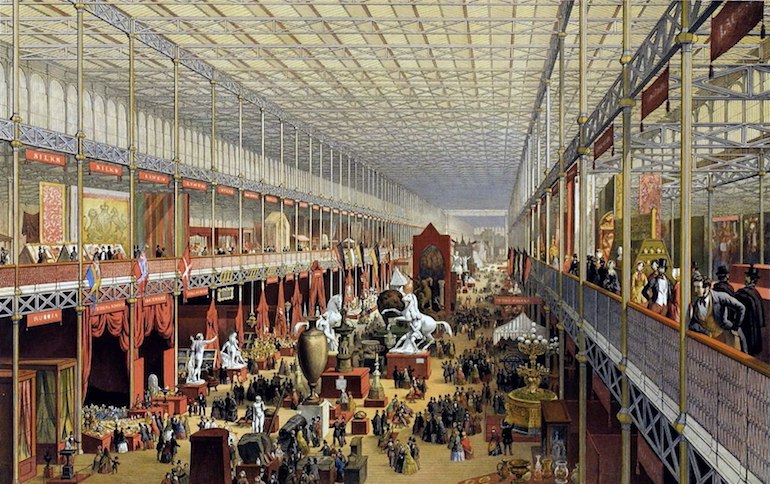

The interior of the Crystal Palace in London during the Great Exhibition of 1851. Photo Credit: © Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons.
Paxton presented his design for a glass and steel structure which could be erected in Hyde Park, where Queen Victoria had given permission for a building to erected to house the Great Exhibition and Paxton’s design soon won widespread approval. It was 1,848 feet long, 408 feet wide and 108 feet high, required 4,500 tons of iron, 60,000 square feet of timber and 293,000 panes of glass. Yet it took 2,000 men just eight months to build and the cost was under £80,000.
Six million people, equivalent to a third of the British population at the time, paid a shilling (five pence) to enter the Crystal Palace and see the Great Exhibition. After the huge success of the Exhibition, the building which housed it could have remained in Hyde Park but Queen Victoria had only given permission for a ‘temporary’ structure there, so a group of businessmen raised the money to take down, move and re-erect it in South London.
The area where it was re-erected soon became known as Crystal Palace and the name was also adopted by the local soccer team, who are nicknamed ‘the glaziers.’ They are currently the only London Premier League team based south of the River Thames.
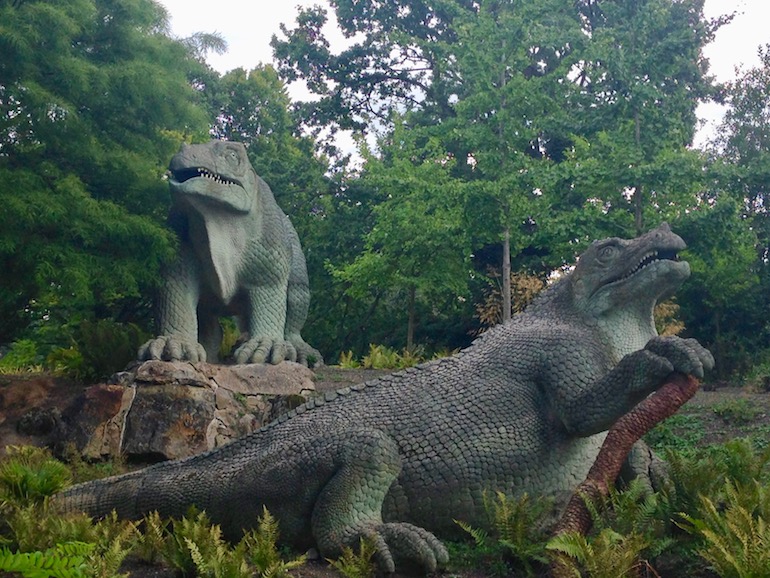

An 1853 model of an Iguanodon; the most recognisable of the Crystal Palace Dinosaurs in London. Photo Credit: © Ursula Petula Barzey.
After it was rebuilt the new Crystal Palace became a popular concert and circus venue and hosted flower and pet shows in which owners could display their cats and dogs in competition. Creatures from an earlier era also appeared as the Dinosaur Court was built on an island near the Palace. These models continue to attract visitors, although they are now showing their age and reflect the limited knowledge of these creatures available at the time.
Sadly, one of London’s most famous buildings was to fall victim to fire on two occasions – in 1866 when the Tropical Gardens were destroyed and £30,000 worth of plants were lost. Then in 1936 a fire engulfed and destroyed the entire building. Workmen had detected smoke but only called the fire brigade when it was too late to save the building from burning down.
Finally, the water towers erected to feed the fountains which had adorned the Crystal Palace Gardens were dismantled at the beginning of the Second World War when it was felt they would provide too obvious a landmark to the Luftwaffe. A small museum (only open on Sundays) tells the story of the building and nearby can be seen a tall television tower, a bust of designer Joseph Paxton as well as statues of dinosaurs and the sphinxes erected to guard the Palace entrances. The rest of one of London’s most iconic lost buildings have all disappeared.
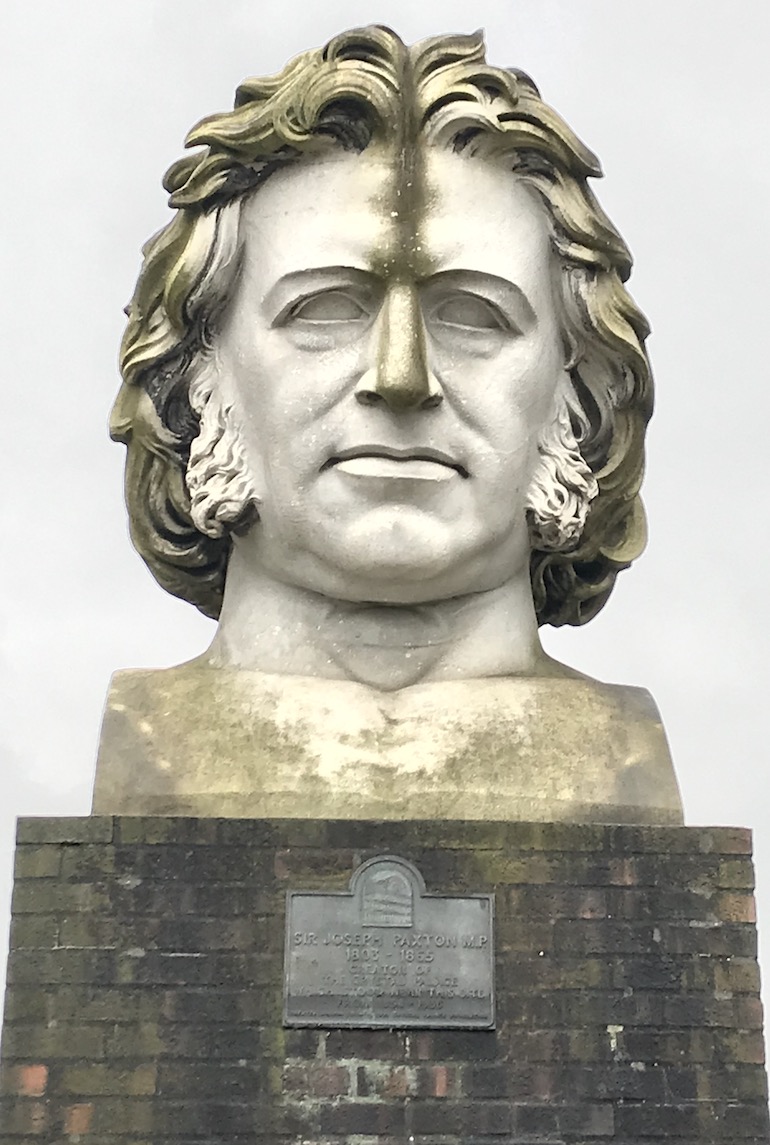

Crystal Palace Paxton bust. Photo Credit: © Edwin Lerner.

Crystal Palace Museum in London. Photo Credit: © Edwin Lerner.
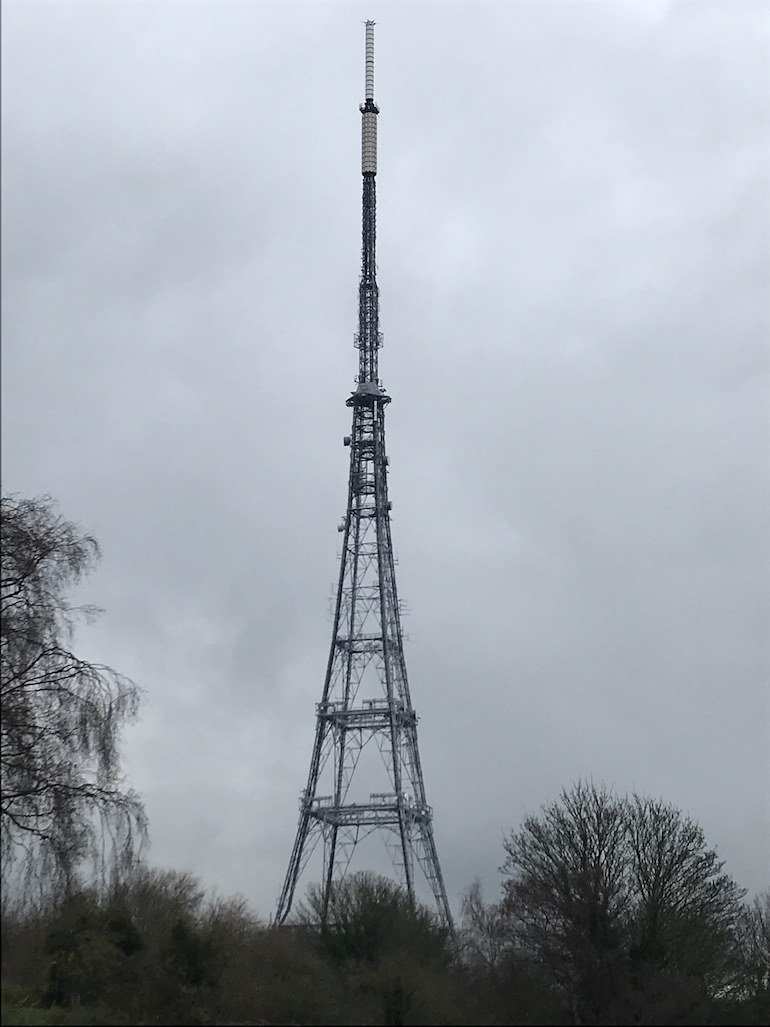

Crystal Palace TV Tower. Photo Credit: © Edwin Turner.






Leave a Reply